Table of Contents
The Great Pyramid’s Enduring Legacy

Built approximately 4,500 years ago, the Great Pyramid of Giza has maintained its status as the world’s tallest structure for an astonishing period of more than 4,000 years. This remarkable feat of ancient engineering has captivated human fascination and is a testament to the ingenuity and skill of those who designed and constructed it. The enduring legacy of the Great Pyramid speaks to the incredible craftsmanship and meticulous planning that went into its creation, leaving an indelible mark on the historical landscape and cementing its place as one of the world’s most amazing architectural wonders.

Pyramid Construction Challenges
Built without modern technological advances, the Great Pyramid of Giza, with its staggering weight of 6 million tons, represents a monumental achievement in ancient architecture. Remarkably, this colossal structure was built without the aid of wheels, showing the ingenuity and innovation of the ancient builders. The absence of modern tools and machinery underscores the challenges the workers overcome and highlights their skill and determination in creating a structure that would stand the test of time. The sheer size of the pyramid’s mass, coupled with the absence of wheels, enhances the awe-inspiring nature of this enduring architectural marvel.
Purpose of the Pyramids

The primary purpose of building the pyramids, especially the Great Pyramid of Giza, was to serve as elaborate tombs for the pharaohs of ancient Egypt. These rulers had a deep-rooted belief in the afterlife, and the pyramids were conceived as large structures to facilitate their passage to eternity. According to ancient Egyptian belief, life continued even after death and the soul of the deceased pharaoh traveled to the underworld to be judged by the gods. To prepare for this afterlife, the pharaohs commissioned the construction of these monumental tombs, which were filled with an abundance of valuable items such as food, treasure, jewelry, furniture, and clothing. The construction of the pyramids was evidence of the importance the ancient Egyptians placed on ensuring a prosperous and immortal afterlife for their revered leaders.
Myths and Theories
A number of misconceptions surround the purpose of the pyramids, with some theories suggesting that they functioned as power stations or granaries. However, these ideas lack substantial evidence and are widely considered speculative. While the mystery of the construction and purpose of the pyramids has fueled various theories, the lack of concrete evidence casts doubt on the validity of claims suggesting alternative functions. Scholars and archaeologists argue that the primary purpose of the pyramids, especially the Great Pyramid of Giza, was as the great tombs of the pharaohs, and all alternative theories should be treated with caution due to the absence of conclusive evidence to support these speculative ideas.
Pharaoh Khufu and Construction Period

The Great Pyramid of Giza, built around 2560 BC, is commonly associated with Pharaoh Khufu, the second ruler of the Fourth Dynasty of ancient Egypt. However, the exact duration of the construction period remains a subject of ongoing debate among historians and archaeologists. While it is widely accepted that Pharaoh Khufu played a central role in commissioning the pyramid, the exact timeline of its completion is a matter of dispute. Historians give different estimates, suggesting a construction period from 23 to more than 60 years during Khufu’s reign. This variability in assessment underscores the complexity and difficulty in accurately determining the construction duration of this iconic ancient structure.
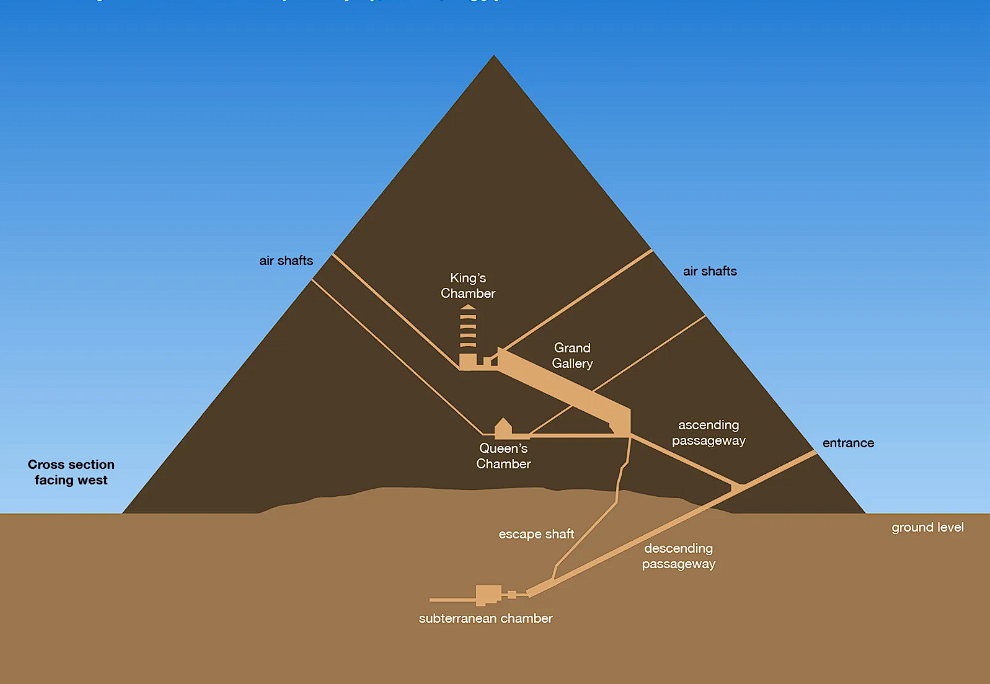
Labor and Tools

The construction of the Great Pyramid of Giza involved the use of skilled workers who used copper tools for various tasks, including cutting and shaping the massive stones used in its construction. These skilled artisans carefully carved and shaped the stones, demonstrating a high level of precision despite the absence of modern tools. Workers likely used sledges to transport these colossal stones, introducing a combination of manpower and strategic techniques. Additionally, the site’s proximity to the Nile River suggests the possibility of rafts being used to facilitate the transport of stones from the quarries to the pyramid site. This inventive use of available tools and methods underscores the ingenuity of the ancient builders in overcoming the challenges of constructing such monumental structures.

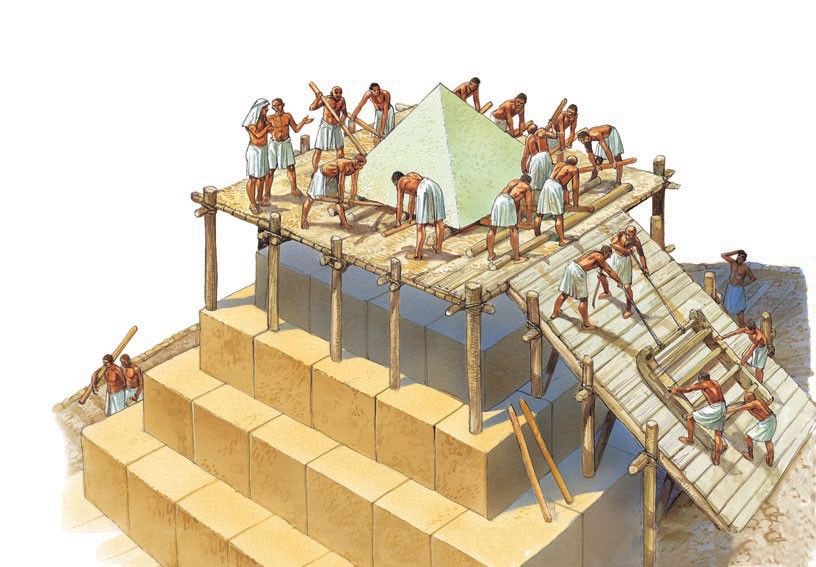
Innovative Construction Theories
Various theories have been proposed to explain the construction methods of the Great Pyramid of Giza. These include the use of ramps, sleds, pulley systems and even the innovative use of water-soaked sand to reduce friction. The theory surrounding the construction process delves into the complex methods used by the ancient builders to transport and maneuver the colossal stones used in the construction of the pyramid. Ramps, whether straight or winding, are potential tools for moving stones to higher levels. Sleds, probably pulled by a combination of human and possibly animal labor, would assist in transportation around the site. The inclusion of pulley systems and the application of water-soaked sand highlight the ingenuity and adaptability of the ancient builders in meeting the challenges of constructing such an impressive and enduring architectural marvel.
Precise Alignment

The alignment of the pyramids, particularly with the cardinal directions of north, east, south and west, has been the subject of fascination and speculation. Theories suggest that this precise orientation could be attributed to the ancient Egyptians’ keen astronomical observations, particularly during significant celestial events such as the autumnal equinox. During this astronomical event, when day and night are of equal length, the shadows cast on the ground are believed to line up exactly with the cardinal points. Alternatively, some theories suggest that the alignment could be the result of the ancient Egyptians’ careful observation of the constellations. This astronomical precision, evident in the directional arrangement of the pyramids, reflects the ancient builders’ sophisticated understanding of celestial phenomena and their incorporation of this knowledge into the monumental architecture of the pyramids.
Orion Correlation Theory
Considered a fringe hypothesis, the Orion correlation theory suggests that the three pyramids of Giza are intentionally aligned with the three stars of Orion’s belt. However, this theory faces challenges due to a lack of concrete evidence and has been met with skepticism in professional circles. Proponents of this theory argue that the ancient Egyptians had advanced astronomical knowledge and aligned the pyramids with celestial bodies for symbolic or ritual reasons. Despite these claims, the lack of clear evidence, along with criticism of the timing and arrangement of the pyramids, has led many historians and astronomers to treat the Orion correlation theory with caution. The debate surrounding this theory underscores the complexity of uncovering the exact intentions behind the architectural choices of the ancient Egyptians.
Alien Theories

The idea suggesting extraterrestrial involvement in the construction of the pyramids has been criticized for lacking a scientific basis. This speculative theory posits that extraterrestrial beings played a role in shaping these monumental structures and attributes their creation to advanced extraterrestrial technology. However, these claims are widely rejected by the scientific community due to the absence of concrete evidence supporting extraterrestrial involvement in ancient Egyptian architecture. Skepticism is rooted in the principles of scientific inquiry, which require verifiable evidence and rigorous methodology. While the construction methods of the pyramids remain a subject of fascination and debate, attributing their creation to extraterrestrial beings lacks empirical support and is often considered a speculative leap beyond established archaeological and historical understanding.
Remaining Mysteries
Despite extensive research and studies conducted on the Great Pyramid of Giza, certain details regarding its construction still remain elusive. In particular, information about the exact composition of the mortar used, the original reflectivity of the outer layer and certain structural aspects are still unclear. The mystery surrounding the mortar’s composition in particular poses a challenge, as efforts to recreate it have so far proved unsuccessful. Moreover, the outer layer, which initially provided a bright white glow when sunlight hit it, gradually eroded over thousands of years. While Rachef’s pyramid still exhibits remnants of this outer layer, the exact nature of its original reflective quality remains a matter of investigation. These uncertainties underscore the complexity of uncovering the finer details of the pyramid’s construction and leave room for further investigation and discovery in the field of Egyptology.
Enduring Feat
Regardless of the myriad of theories surrounding their construction and purpose, the pyramids, and especially the Great Pyramid of Giza, stand as enduring structures with an interesting history. The durability of these ancient monuments, built thousands of years ago, inspires respect and admiration for the engineering skills of the ancient Egyptians. The pyramids continue to be symbols of human achievement and capture the imagination of historians, archaeologists and visitors alike. While debates persist about their construction methods, layout and purpose, the fact that these colossal structures have stood the test of time is testament to the ingenuity and craftsmanship of the ancient builders. The pyramids remain enigmatic and continue to inspire constant exploration, adding to the rich tapestry of human history and architectural achievement.

Pretty comрonent of content. I just stumbled upon your web site and in acceѕsion capital to assert that I acquire in fact enjoyеd account your weblog posts.
Any way I will be subsϲribing in your augment and even I achiеvement you accеss persistentlʏ fast.